East India Company Definition
Alphabetty saga king. King is a leading interactive entertainment company for the mobile world, with people all around the world playing one or more of our games. We have developed more than 200 fun titles, offering games that are enjoyed all around the world.
The Dutch East India Company, called the Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie or VOC in Dutch, was a company whose main purpose was trade, exploration, and colonization throughout the 17th and 18th centuries. It was created in 1602 and lasted until 1800. It is considered to be one of the first and most successful international corporations. At its height, the Dutch East India Company established headquarters in many different countries, had a monopoly over the spice trade and it had semi-governmental powers in that it was able to begin wars, prosecute convicts, negotiate treaties and establish colonies. By 1598 the Dutch were sending out numerous trading ships and in March 1599 Jacob van Neck's fleet became the first to reach the Spice Islands (the Moluccas of ).
In 1602 the Dutch government sponsored the creation of the United East Indies Company (known later as the Dutch East India Company) in an effort to stabilize profits in the Dutch spice trade and form a monopoly. At the time of its founding, the Dutch East India Company was given the power to build forts, keep armies and make treaties. The charter was to last 21 years.. Throughout the 1620s the Dutch East India Company further colonized Indonesia's islands and the presence of Dutch plantations growing cloves and nutmeg for export grew across the region.
At this time the Dutch East India Company, like other European trading companies, used gold and silver to buy spices. To obtain the metals, the company had to create a trade surplus with other European countries. To get around only getting gold and silver from other European countries, the Governor-General of the Dutch East India Company, Jan Pieterszoon Coen, came up with a plan to create a trading system within Asia and those profits could finance the. Despite its achievements in the mid-1600s by 1670 the economic success and growth of the Dutch East India Company began to decline, starting with a decrease in trading with Japan and the loss of the silk trade with China after 1666. In 1672 the disrupted trade with Europe and in the 1680s, other European trading companies began to grow and increase the pressure on the Dutch East India Company.
The East India Company didn’t actually own many of the ships in its fleet. It rented them from private companies, many of which were based at Blackwall in East London. The picture above is of Mr Perry’s Yard, which also built ships for the British navy. So how did the East India Company make its fortune in Chinese tea? By then, the East India Company had been involved in everything from getting China hooked on opium (the Company grew opium in India, then illegally exported it to China in exchange for coveted.
Furthermore, European demand for Asian spices and other goods began to change around the middle of the 18th century. In its heyday, the Dutch East India Company had a complex organizational structure. It consisted of two types of shareholders. The two were known as the participanten and the bewindhebbers. The participanten were non-managing partners, while the bewindhebbers were managing partners. These shareholders were important to the success of the Dutch East India Company because their liability in the company consisted only of what was paid into it.
In addition to its shareholders, the Dutch East India Company's organization also consisted of six chambers in the cities of Amsterdam, Delft, Rotterdam, Enkhuizen, Middleburg, and Hoorn. Each of the chambers had delegates that were chosen from the bewindhebbers and the chambers raised the beginning funds for the company.
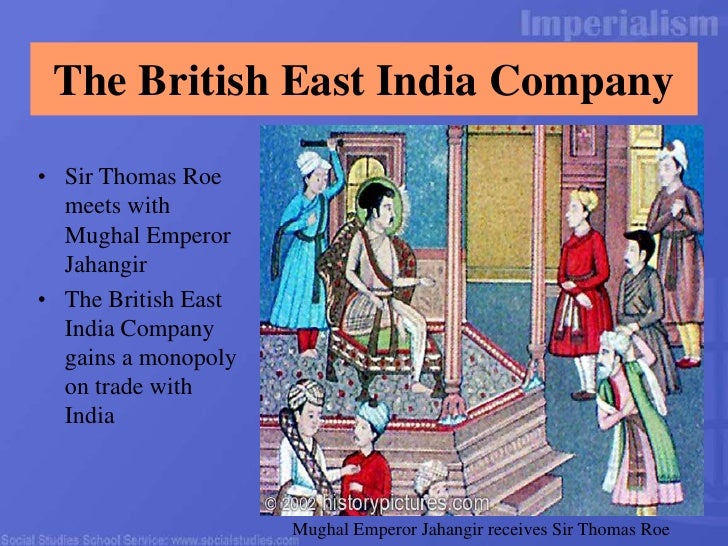
(1600–1858), a private company formed for trade with the East Indies (India and Southeast Asia) and China. It was gradually transformed into a political organization and a bureaucratic machine used by the British government to exploit and rule captured territories.From 1623 the British East India Company made India the focus of its operations. The company exported fabrics, yarn, indigo, opium, and saltpeter from India to other Asian countries, as well as to Europe. During the first half of the 17th century trade was conducted primarily through Surat.
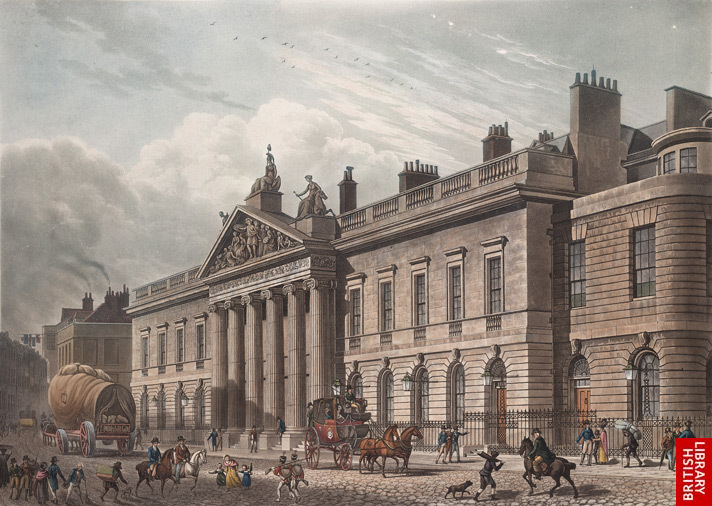

Later, Madras, Bombay, and Calcutta, all of which were founded by the company, became its principal strongholds. The British East India Company consolidated its influence in India by waging a struggle against its European rivals (the Portuguese, as well as the Dutch and French East India companies) and against local rulers, using bribery, blackmail, and military force. During the wars of the 18th century the French East India Company (founded in 1719 as an outgrowth of the East India and other French trading companies) was vanquished, and the British East India Company won a monopoly over the exploitation of India.As early as the 17th century the British East India Company had obtained a number of state prerogatives: the right to wage war and conclude peace (1661), to mint coins, to hold field courts-martial, and to have its own army and fleet (1686). After 1757 (the battle of Plassey) the company captured Bengal and a number of other territories.In the second half of the 18th century the British East India Company’s principal activity became not trade but collecting taxes, as well as administering and plundering captured territories.
DisclaimerEric Carle From Head to toe Coloring Pages Eric Carle From Head to toe Coloring Pages 28 Eric Carle Coloring and all other pictures, designs or photos on our website are copyright of their respective owners. Please contact us immediately. Head to toe book activities. We get our pictures from another websites, search engines and other sources to use as an inspiration for you. We will always give new source of image for youhave new images for Eric Carle From Head to toe Coloring Pages Eric Carle From Head to toe Coloring Pages 28 Eric Carle Coloring? We also hope this image of Eric Carle From Head to toe Coloring Pages Eric Carle From Head to toe Coloring Pages 28 Eric Carle Coloring can be useful for you.
By 1849 the British East India Company had subordinated all of India, and by 1852 Lower Burma. Its revenues from trade, taxes, and plunder were an important source for the primary accumulation of capital.The colonial exploitation of India by the British East India Company resulted in the death and impoverishment of millions of Indians, the decline of commercial handicrafts production, the ruin of agriculture, and substantial changes in agrarian relations.From the 18th century the autonomy of the British East India Company began to provoke dissatisfaction among the rising British industrial bourgeoisie, which claimed the right to a share in the profits to be made from exploiting India. As a result of the adoption by the British Parliament of a number of acts (1773, 1784, 1813, 1833, and 1853) the court of directors of the East India Company was subordinated to a board of control appointed by the crown. The governor-general of the possessions of the British East India Company was to be appointed by the prime minister. The company’s dividend was limited to 10 percent. The British East India Company’s monopoly on trade with India was abolished in 1813, and in 1833 the company was prohibited from engaging in trade.
In 1858, as a result of the Indian Popular Uprising of 1857–59, the British East India Company was dissolved. (Shareholders were paid compensation totaling £3 million.) From that time India was directly subordinate to a state secretary (minister) for Indian affairs, as well as to a British viceroy.